What is filariasis ?
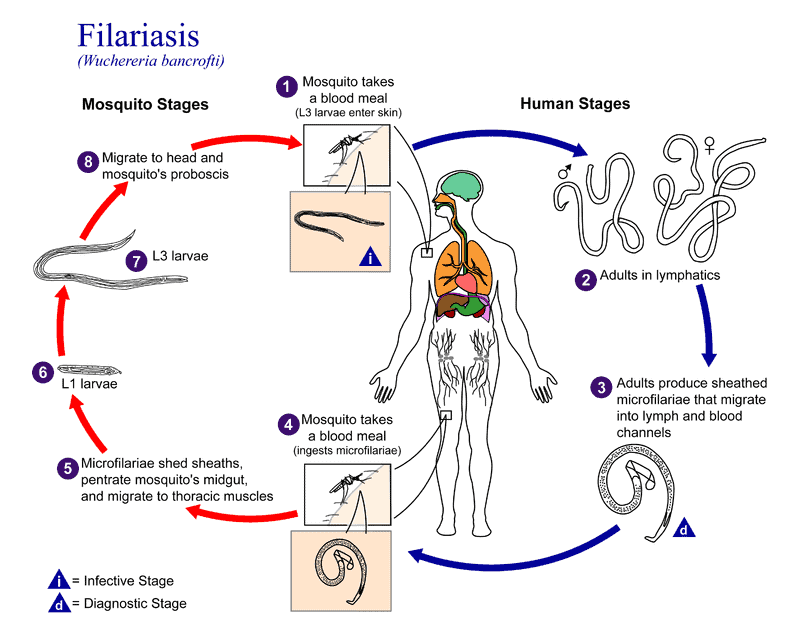
Filariasis is a chronic disease caused by parasitic filarial worms (a group of parasitic nematodes transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods) that live in the human lymphatic system, subcutaneous tissue, abdominal cavity, and thoracic cavity.
There are two main types of filariasis: bancroftian filariasis and filariasis malayi, caused by infection with Bancroftian filariasis and filariasis malayi, respectively. The clinical manifestations of these two types of filariasis are very similar, with the acute phase showing recurrent episodes of lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, and fever, and the chronic phase showing lymphedema, elephantiasis, and scrotal effusion, which can lead to physical deformity, disability, social discrimination, and poverty.
Resource:Wikipedia
Common diagnostic methods of filariasis
(1) Blood test: Microfilariae detection from peripheral blood is the most reliable method to diagnose filariasis. Since microfilariae have a nocturnal periodicity, the time of blood collection from 9:00 p.m. to 2:00 a.m. the next morning is appropriate. The thick blood film method, fresh blood drops method, concentration method or sea swarm raw daytime induced method can be used.
(2) Body fluid and urine examination: Microfilariae can also be seen in various body fluids and urine, such as syringomyelia, lymphatic fluid, ascites, celiac disease, etc. Direct smear method, centrifugal concentration method or membrane filtration concentration method can be used.
(3) Biopsy: cut biopsies from subcutaneous tissues or lymph nodes and observe with microscope whether adult worms or microfilariae are present. This method is suitable for patients without microfilariae in the blood, but it requires surgical operation and is more complicated.
(4) Immunological examination: diagnosis of filarial infection by detecting specific antibodies or antigens in the serum. This method can distinguish different types of filarial infections and determine the degree and stage of infection, but may be interfered with by other parasitic infections.
Introduction to rapid diagnosis of filarial worms
The filarial rapid diagnostic test is a test based on the principle of immunochromatography that can diagnose filarial infection by detecting specific antibodies or antigens in a blood sample within 10 minutes. Compared to the traditional microscopic examination of microfilariae, the filarial rapid diagnostic test has the following advantages:
– No time limit on blood collection, allowing testing at any time of day without the need to collect blood samples at night
– No complex equipment or specialized personnel are required; the results can be determined by simply dropping blood onto a test card and observing for the appearance of color bands.
– It is not interfered by other parasitic infections and can accurately distinguish between different types of filarial infections and determine the degree and stage of infection.
– It can be used for mass screening and epidemiological monitoring, as well as to assess the effectiveness of preventive chemotherapy.
Resource:World Health Organization
Recommended products for filarial rapid diagnosis
The use of filarial rapid diagnostic tests can improve diagnostic efficiency and accuracy, facilitating the timely detection and treatment of infected individuals, thereby controlling and eliminating this ancient and highly dangerous parasitic disease.
Bio-mapper’s filarial rapid diagnostic products allow for rapid and accurate detection of this disease.